Related Posts
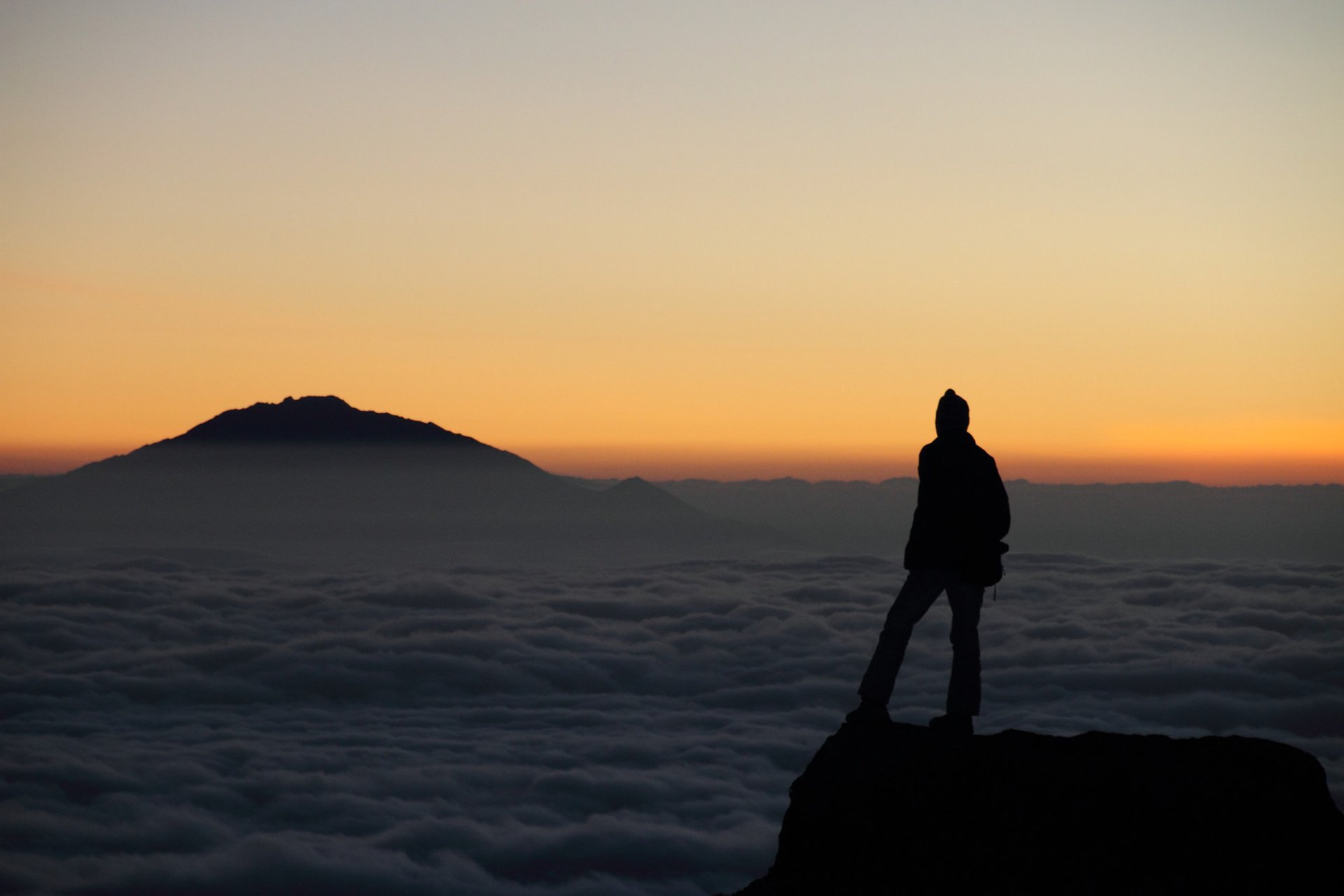

May 01, 2024 4 mins read
An Altitude Reality Check on Kilimanjaro: The Mountain of Greatness
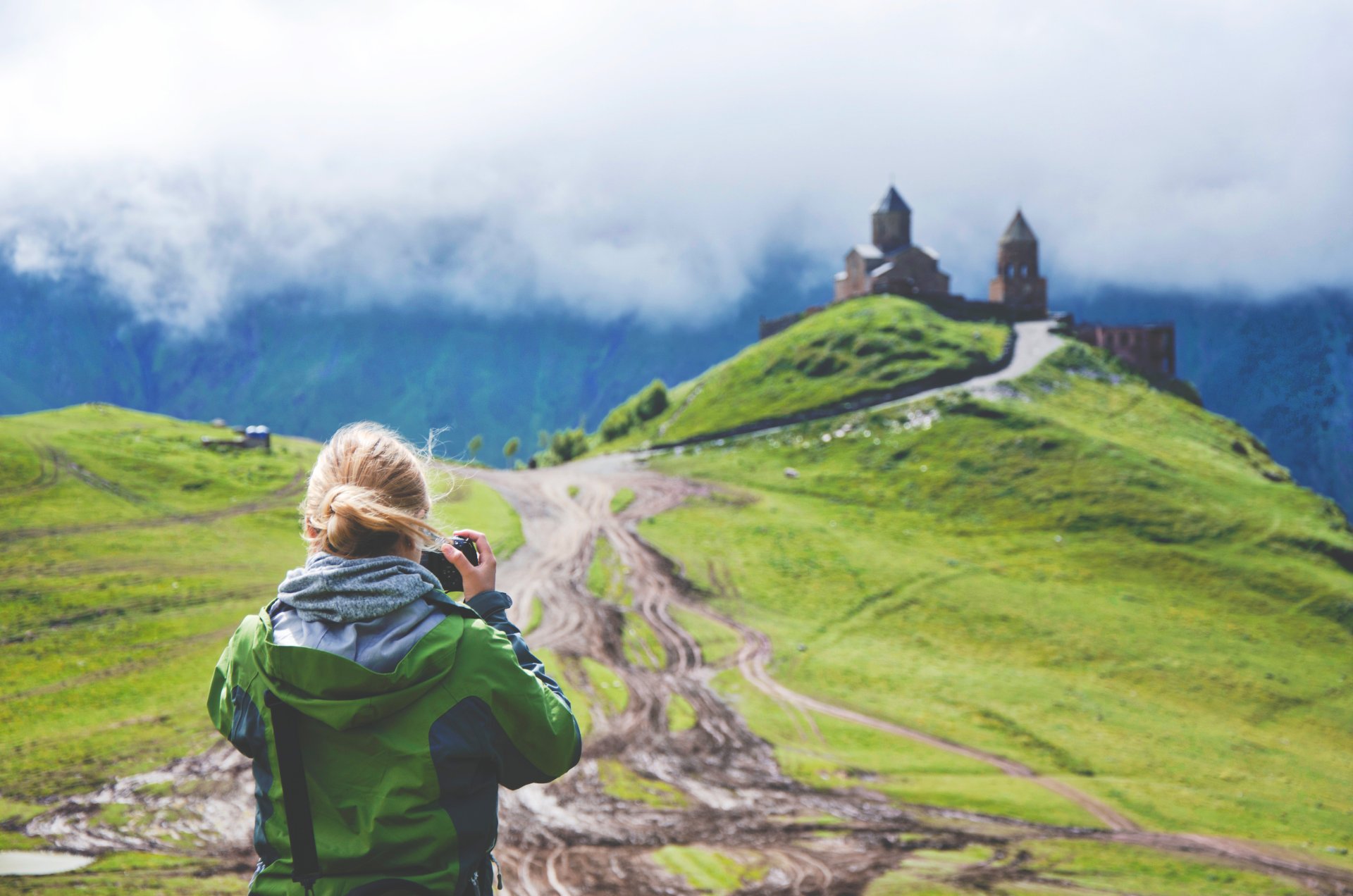

Apr 24, 2024 8 mins read
Are More Women Traveling Without Men?
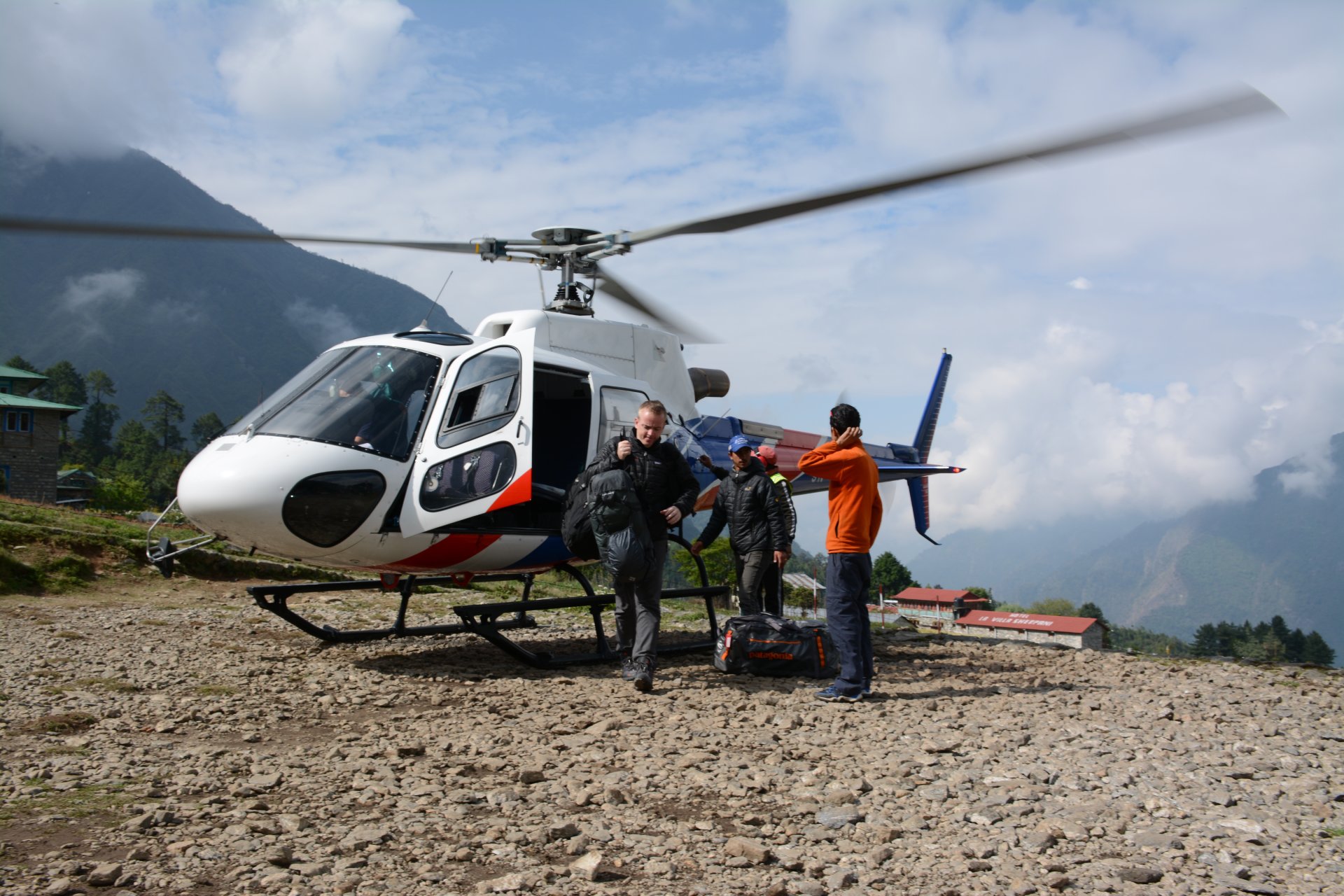

Apr 18, 2024 2 mins read
Rescue Experts in Action: Saving High-Altitude Climbers
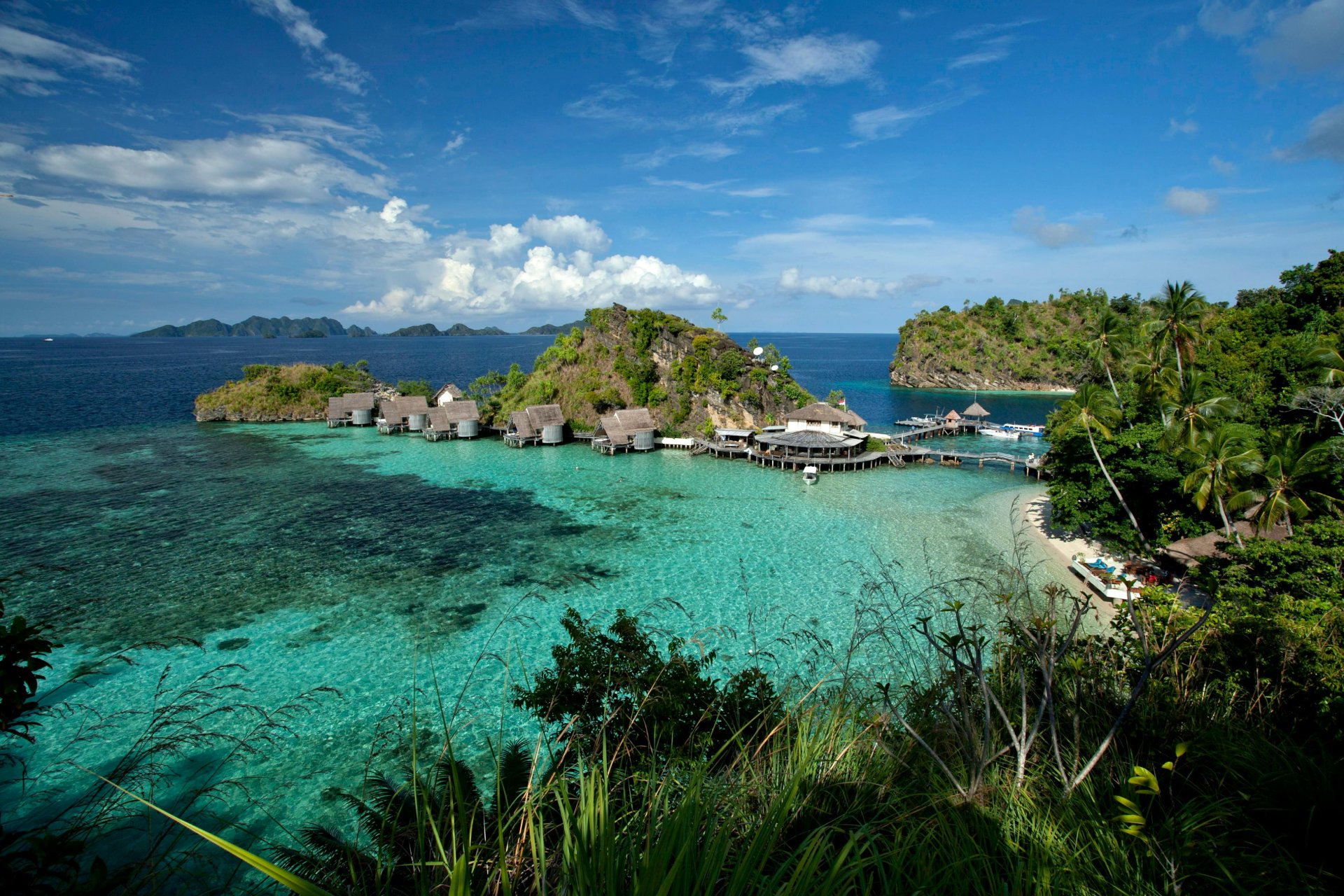

Apr 16, 2024 4 mins read
Mission Briefs: Global Rescue In Action – April

Apr 03, 2024 6 mins read
A Pedestrian’s Painful Misstep in Portugal

Mar 27, 2024 6 mins read
Shirts On, Heels Off: Unique Laws International Travelers Should Know Before They Go

Mar 21, 2024 4 mins read
Mission Briefs: Global Rescue In Action – March
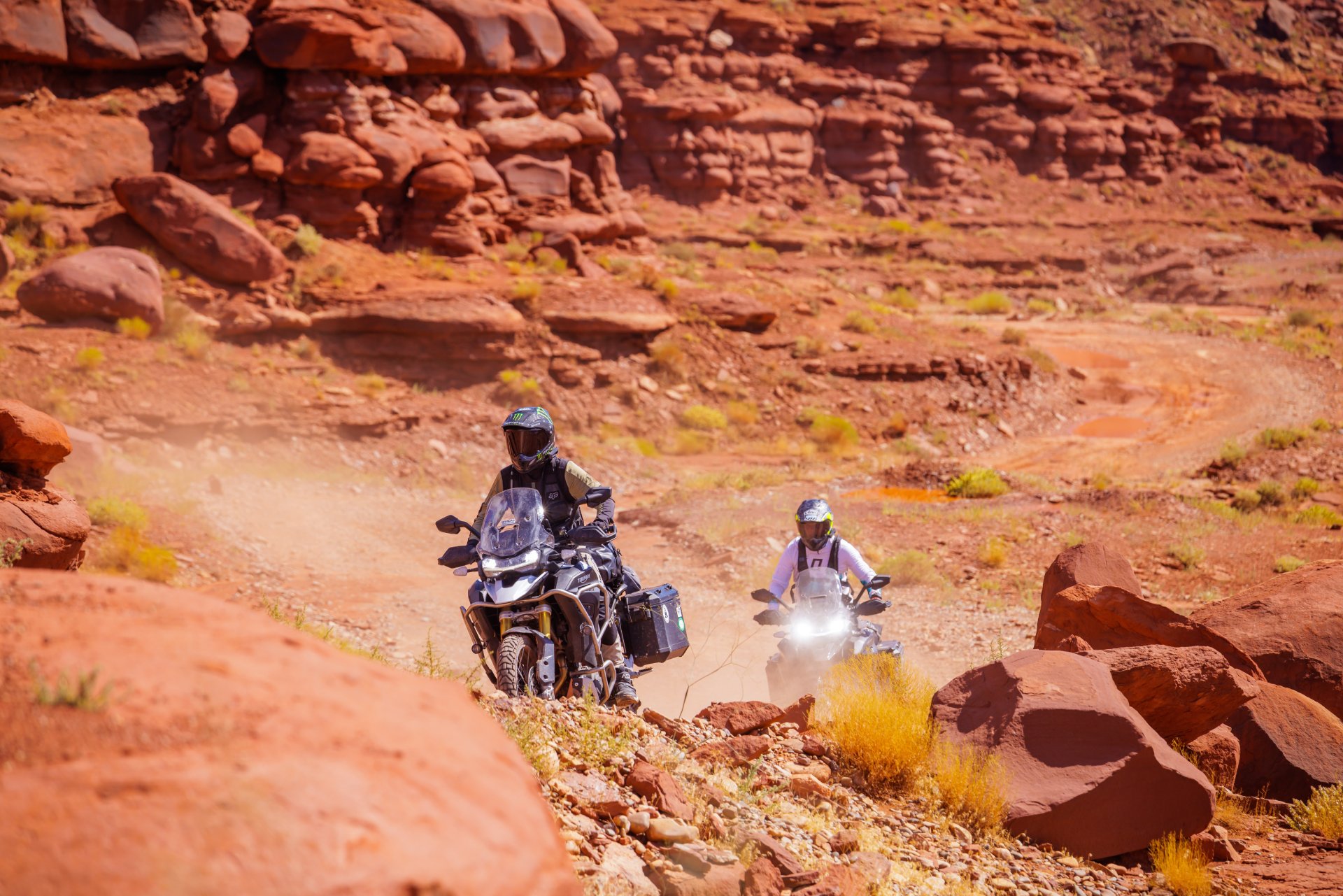

Mar 13, 2024 7 mins read
Beyond the Road: Adventure Motorcycle Touring Surges
General TotalCare Disclaimer:
- ©2024 Global Rescue LLC. TotalCare and the TotalCare logo are service marks of Global Rescue LLC. All Rights Reserved. Global Rescue LLC provides technical and administrative services to Elite Medical Group, P.C. (“Elite Medical”), a professional corporation owned by licensed physicians that employs or contracts with physicians licensed to practice medicine where medical services are provided. It is not guaranteed that a prescription will be written, nor will any DEA controlled substances, non-therapeutic drugs and certain other drugs which may be harmful because of their potential for abuse, as a result of a TotalCare consultation. Elite Medical physicians reserve the right to deny care for potential or actual misuse of services. The Global Rescue Mobile App is designed for operation on the current versions of Android and iOS operating systems. Availability of services is subject to your equipment compatibility, connectivity and signal in your location. There is no guarantee that all features and functionality will be available in your location. Use and availability of the Mobile App is subject to your service provider’s plan and may be subject to additional fees from your provider.
Extended Plan TotalCareSM:
- For individuals 85+, medical transport is not included in membership. Members 85+ may purchase medical transport on a fee for service basis.
Mobile Apps:
- Global Rescue Mobile Apps are designed for operation on the current versions of Android and iOS operating systems. Availability of services is subject to your equipment compatibility, connectivity and signal in your location. There is no guarantee that all features and functionality will be available in your location. Use and availability of the Mobile Apps are subject to your service provider’s plan and may be subject to additional fees from your provider. The download and use of a Global Rescue Mobile App is subject to the terms of your Member Services Agreement and the applicable End User License Agreement (EULA).
Mobile Apps:
- Global Rescue Mobile Apps are designed for operation on the current versions of Android and iOS operating systems. Availability of services is subject to your equipment compatibility, connectivity and signal in your location. There is no guarantee that all features and functionality will be available in your location. Use and availability of the Mobile Apps are subject to your service provider’s plan and may be subject to additional fees from your provider. The download and use of a Global Rescue Mobile App is subject to the terms of your Member Services Agreement and the applicable End User License Agreement (EULA).